 |
Figure 2. Carbon fiber.
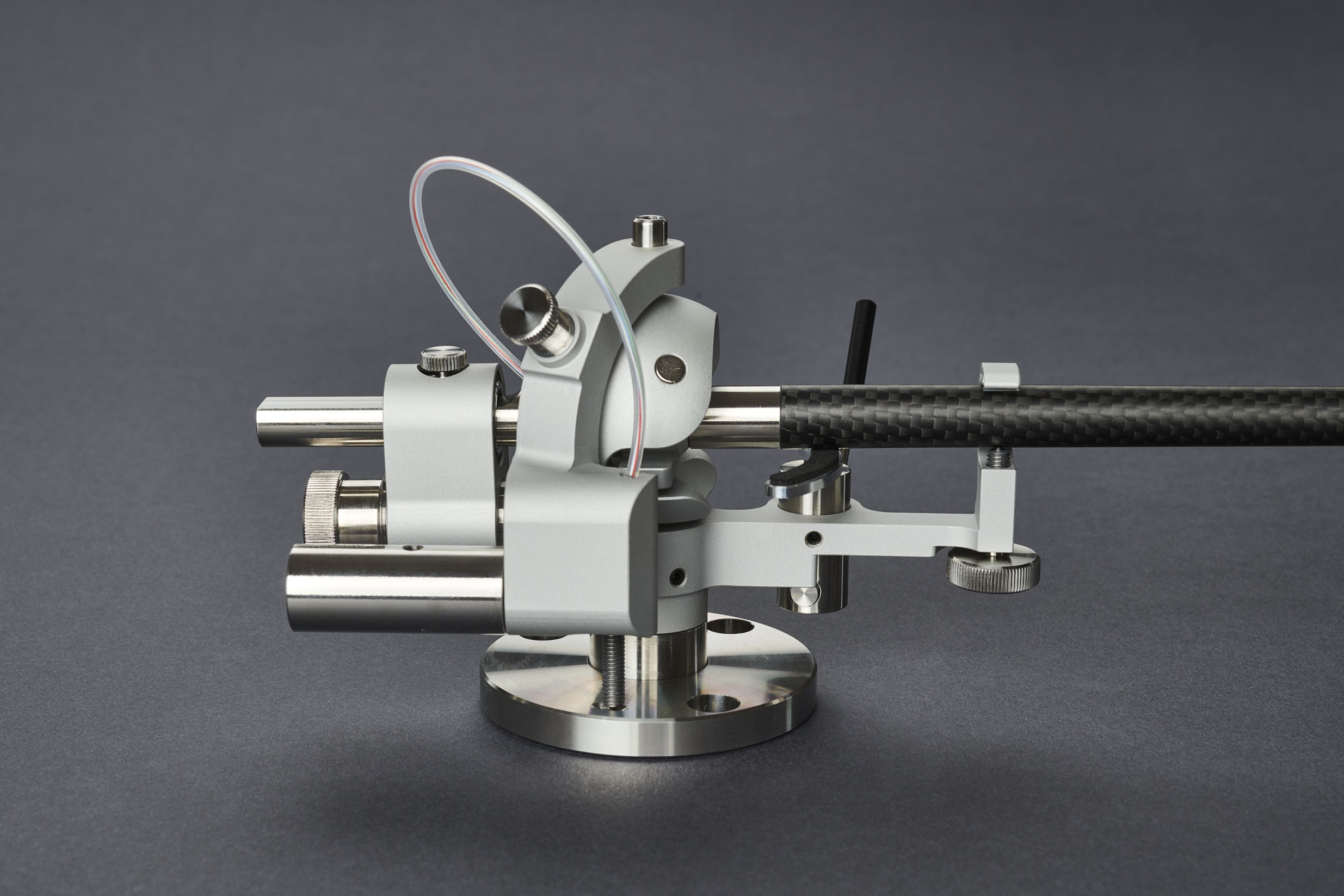
Reed 1H has a cardanic bearing system: vertical axis has thrust rotation bearings and horizontal axis is based on thrust pivot bearings (same concept as in Reed 3P). Such bearing construction eliminates wobbling of a bearing, which has a great impact on the quality of the sound.
Among other features, Reed 1H tonearm has azimuth adjustment, replaceable headshell a... [more]
| Tonearm |  |
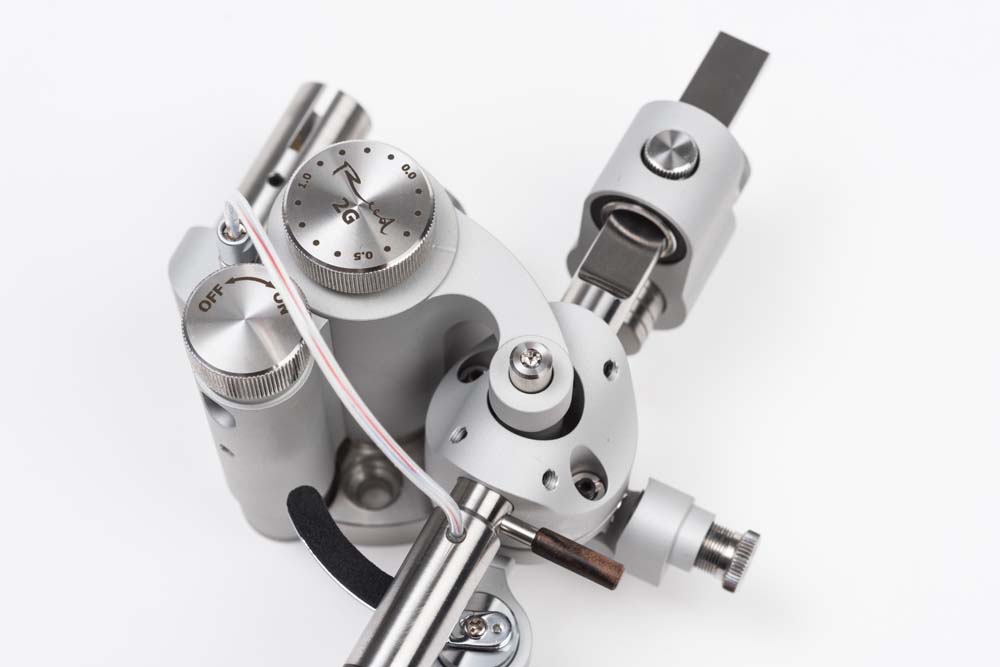 |
Reed 2G with the laser option
Laser-enabled Reed 2G version continues tradition of Reed 3Q and helps audio enthusiasts to set up their systems using latest technology. Calibrated laser add-on, used in this tonearm version, allows user to adjust VTA and azimuth quickly and precisely.
... [more]
| Tonearm |  |
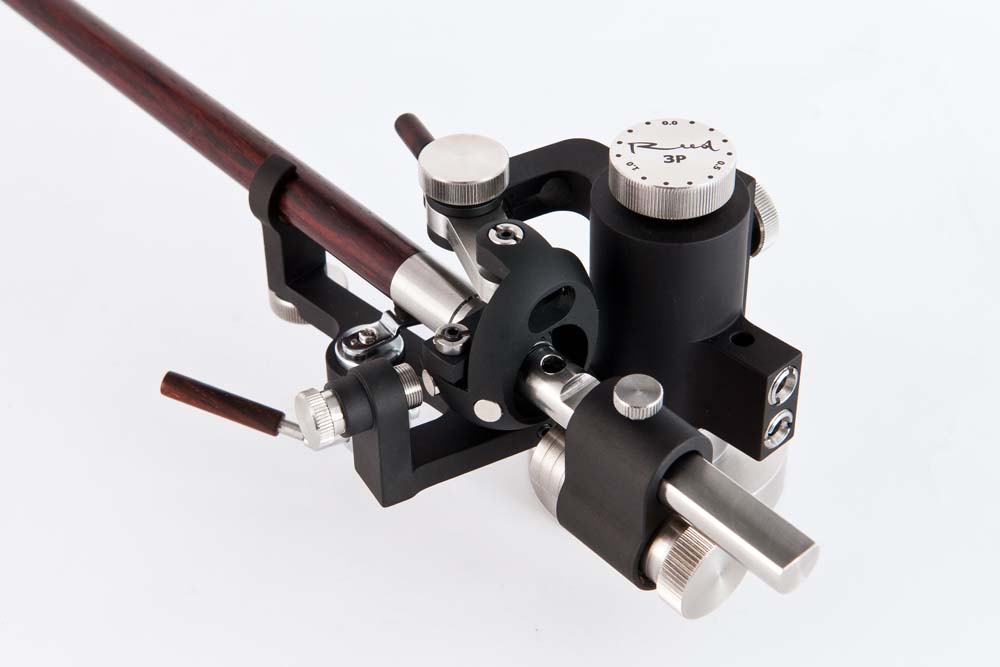 |
Another 3Ps innovation is its bearing system. Although tonearm bearing system can be considered as gimbal, it acts like unipivot one. However, major difference from unipivot system is that instead of a single pivot three pivots and both vertical and horizontal axis’ magnetic stabilizers are used. Such bearing system is as rigid as gimbal, but its friction coefficient is as low as in unipi... [more]
| Tonearm |  |
 |
P1, O1, P3 – Thales’ semicircle,
P1-A1-P3, P1-A2-P3, P1-A3-P3 angles are 90⁰ each,
A1,1B1 = A2,1B2= A3,1B3 segments represent tonearm length,
1B – vertical axis of the tonearm,
1P2 – center of the circle, which is drawn through three points -1B1,1B2,1B3,- axis of rotation of the back link component
2P2 – center of the circle, which is drawn th... [more]
| Tonearm |  |
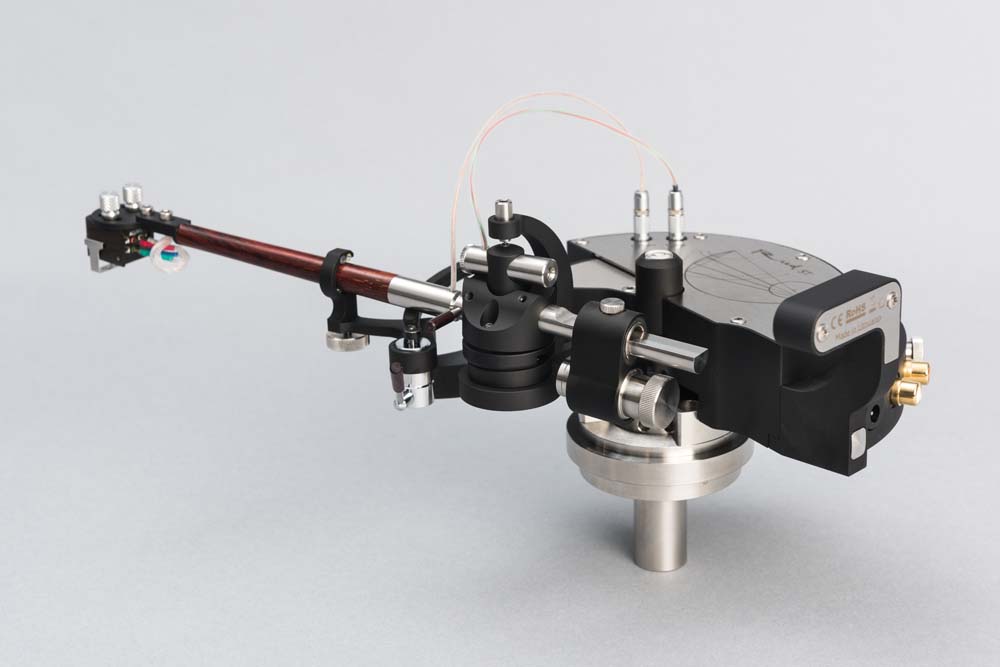 |
P1, O1, P3 – Thales’ semicircle,
Angles P1-A1-P3, P1-A2-P3, P1-A3-P3 are 90 degrees each,
Segments A1B1 = A2B2= A3B3 represent length of a tonearm,
B – Tonearm vertical axis,
P2 represents a center of circle, drawn through three points – B1,B2 and B3 (tonearm ro... [more]
| Tonearm |  |
 | | Turntable |  |























